state-wide information
2021 PURDUE STUDY: Indiana Renewable Energy Community Planning Survey and Ordinance Inventory Summary
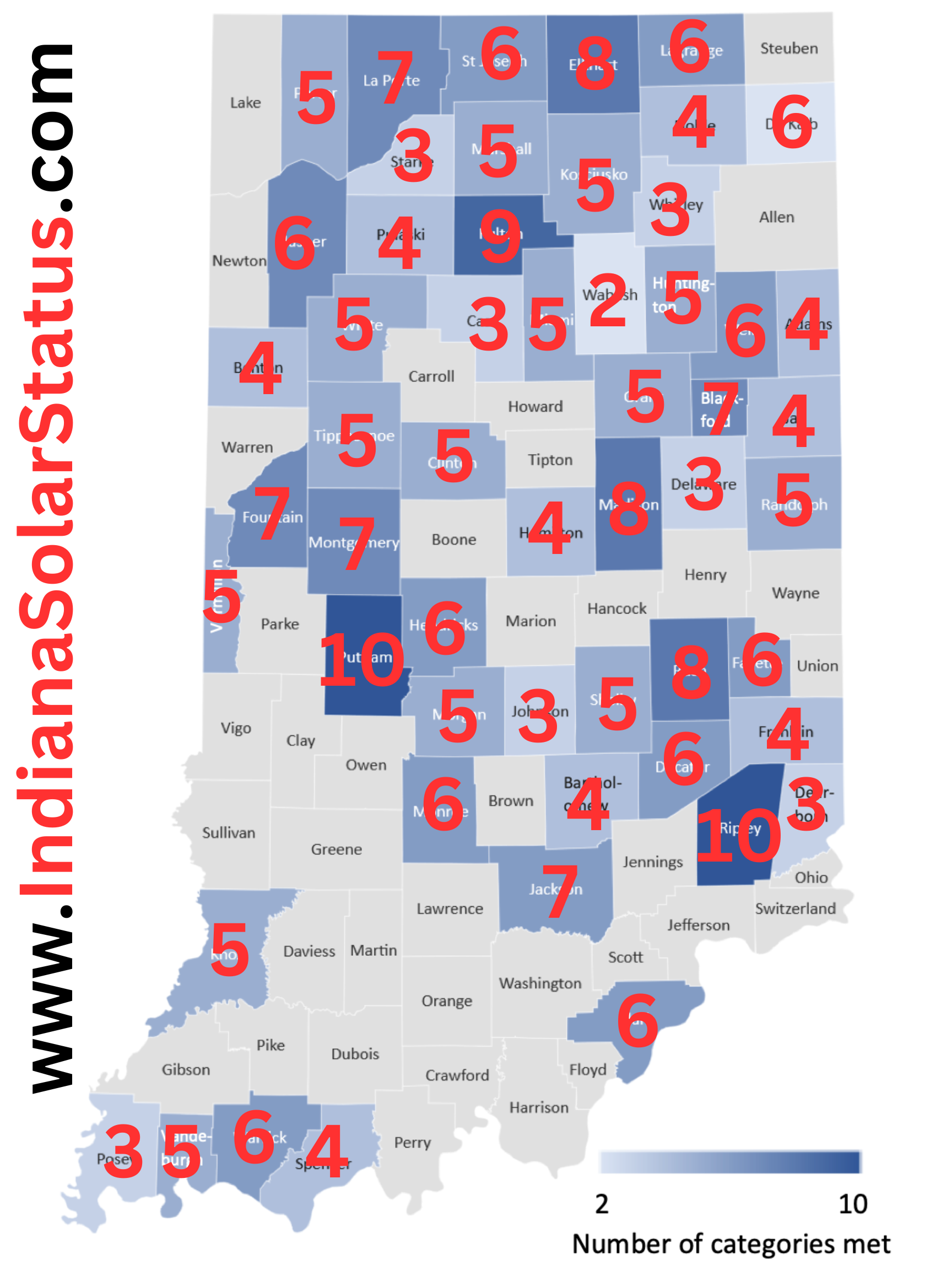
Indiana Counties color coded based on eleven (11) metrics favorable to utility-scale solar according to the linked Purdue study. CLICK HERE
2022 PURDUE STUDY: County Zoning Ordinances for Commercial Solar Compared to Indiana’s Solar Energy Ready Community Standards
Indiana Counties color coded based on use regulations for commercial wind and solar according to the linked Purdue study. CLICK HERE
Map of many utility scale solar projects Operating, Under Development and Under Construction. CLICK HERE
Map of all Residential, Commercial, Institutional, Government, Agricultural/Farm, Utility Company solar panels. CLICK HERE
Interactive map and list of 107 projects in Indiana totaling 1,977 MW. (Many projects identified by Indiana Solar Status are not included on this site.) CLICK HERE
SECTION 1. IC 8-1-41 Chapter 41. Default Standards for Wind Power Devices (Amended July 1, 2022)
SECTION 2. IC 8-1-42 Chapter 42. Default Standards for Commercial Solar Energy Systems (Amended July 1, 2022)
The Indiana General Assembly passed Senate Bill 411 in the spring of 2022, creating voluntary commercial solar regulation standards. Communities that adopt these voluntary standards or have less restrictive standards regulating commercial solar development can qualify as a solar energy ready community. The legislation lays out nine categories of standards, including (1) setbacks, height, and buffers, (2) ground cover, (3) fencing, (4) underground cables and aboveground infrastructure, (5) glare minimization, (6) signal interference, (7) sound level limitations, (8) drainage repair, and (9) decommissioning, abandonment, and "force majeure event." CLICK HERE
KEYWORD DEFINITIONS:
Buffer: Separation distance between two uses or a use and zoning district or municipality. Used as a tool to reduce land use conflict between uses often considered incompatible.
Commercial Solar Energy System (CSES): A use defined within a local zoning ordinance that generally consists of all necessary devices to convert solar energy into electricity. Commercial SESs may be defined as producing energy delivered to a utility's transmission lines or for off-site use. Their size may also delineate commercial SESs in the zoning ordinance from small-scale or personal SESs.
Commercial Wind Energy Conversion System (CWECs): A use defined within a local zoning ordinance that generally consists of all necessary devices to convert wind energy into electricity. Commercial WECs may be defined as producing energy delivered to a utility’s transmission lines or for off-site use. Their size may also delineate commercial WECs in the zoning ordinance from small-scale or personal WECs.
Decommissioning Plan: Decommissioning plans provide specifications on how the renewable energy structure will be removed and the land restored at the end of its useful life. Counties may have various requirements for decommissioning and often require a surety bond or letter of credit from the renewable energy company to ensure decommissioning costs are covered.
Development plan review: A process by which a plan commission, committee, or staff reviews an applicant'sdevelopment plan to ensure the predetermined standards on the zoning ordinance have been met as allowed by IC 36-7-4-1401.5.
Economic Development Agreement (EDA): An agreement between the county and developer to various conditions such as the completion of the project, payments to the county, investments in infrastructure, and incentives.
Ordinance: A law, statute or regulation enacted by a local government unit. For this study, ordinance will refer to a jurisdiction’s zoning ordinance.
Reciprocal buffer: A standard that requires that new uses, i.e. residences, follow the same buffer as required of a new renewable energy development to that buffered use.
Screening: Provides a visual barrier between a use and adjoining properties. Shelterbelts, fencing, or earthen mounds are some of the methods of use.
Setback: The distance from building/improvements from the property line or specified right of way.
Special Exception: Also sometimes referred to as conditional use or special use. Generally understood to be a use of property that is allowed under a zoning ordinance under special conditions – something that needs to be considered on a site-specific base- and must be approved by the board of zoning appeals.
Standards: Provisions of the zoning ordinance regulating the characteristics of development of a particular use or zoning district.
Site plan: A scaled drawing that shows the placement of buildings and infrastructure of a development. Zoning: Land use regulations enacted by a local jurisidiction as a tool to implement their comprehensive plan.
Zoning District: Designated districts based on the predominant use of land (e.g. residential, commercial, industrial, and agricultural). Each district has a set of uses that are permitted by right or by special exception and a set of standards which determine he character of the district.